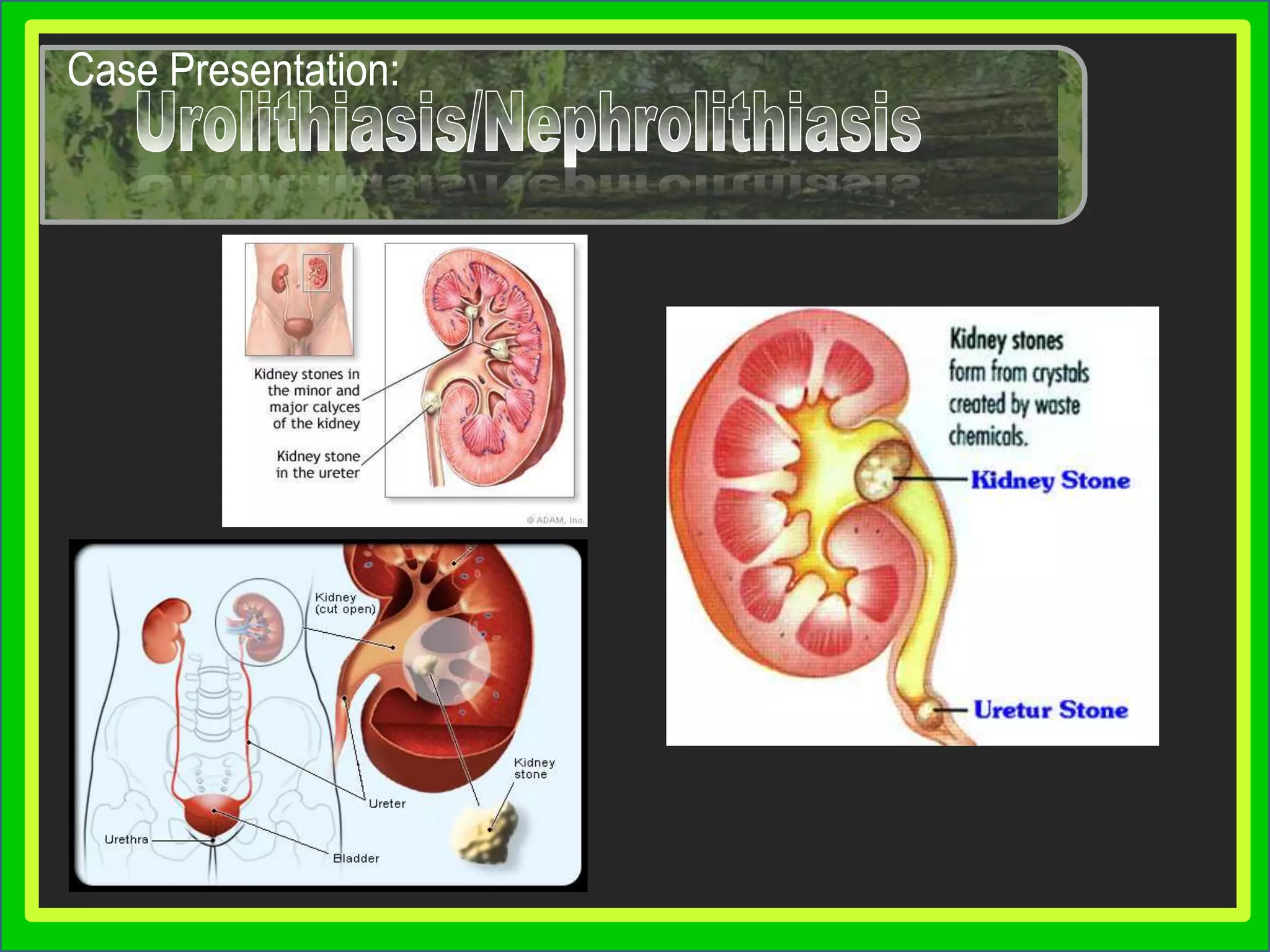
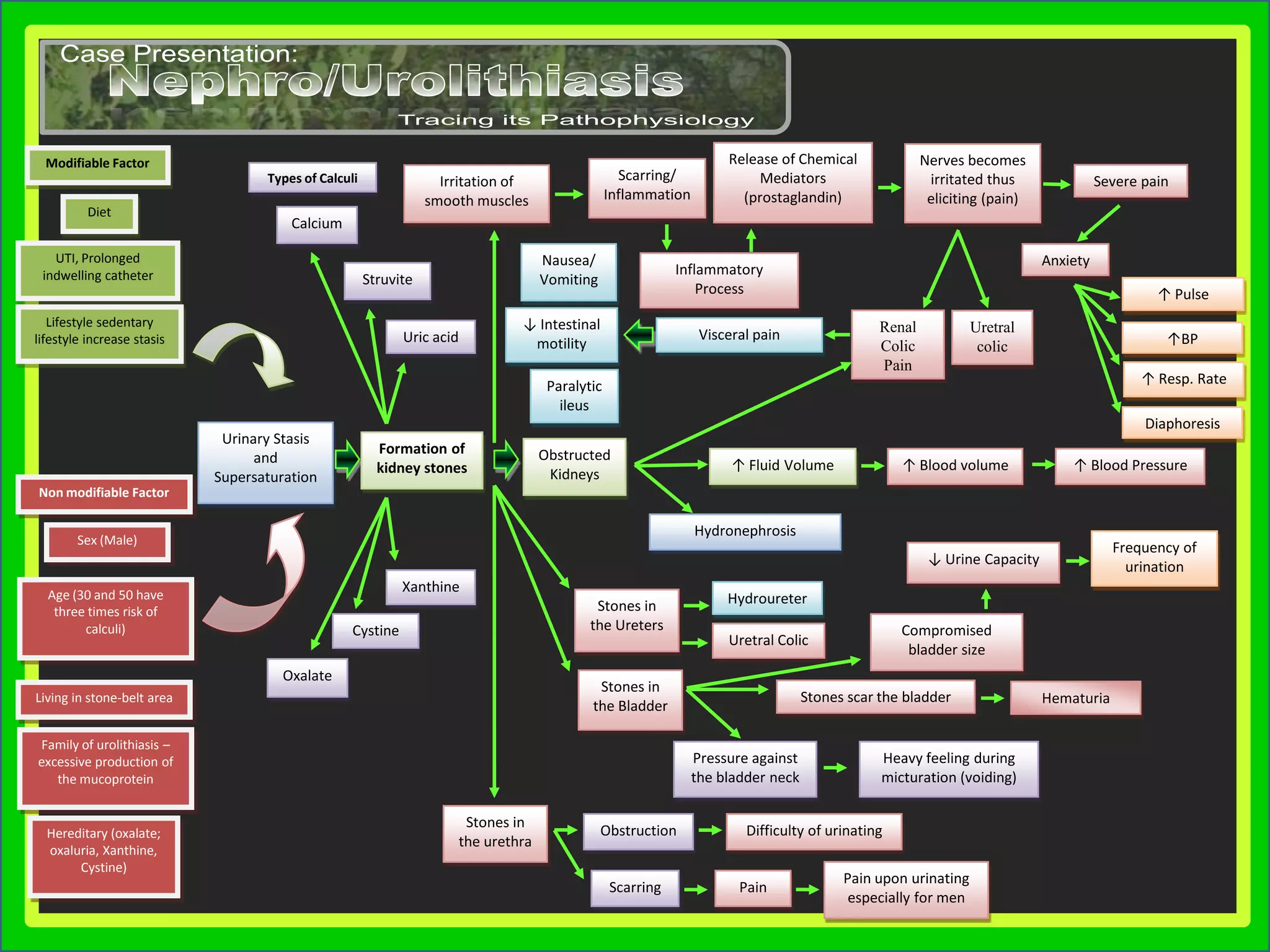
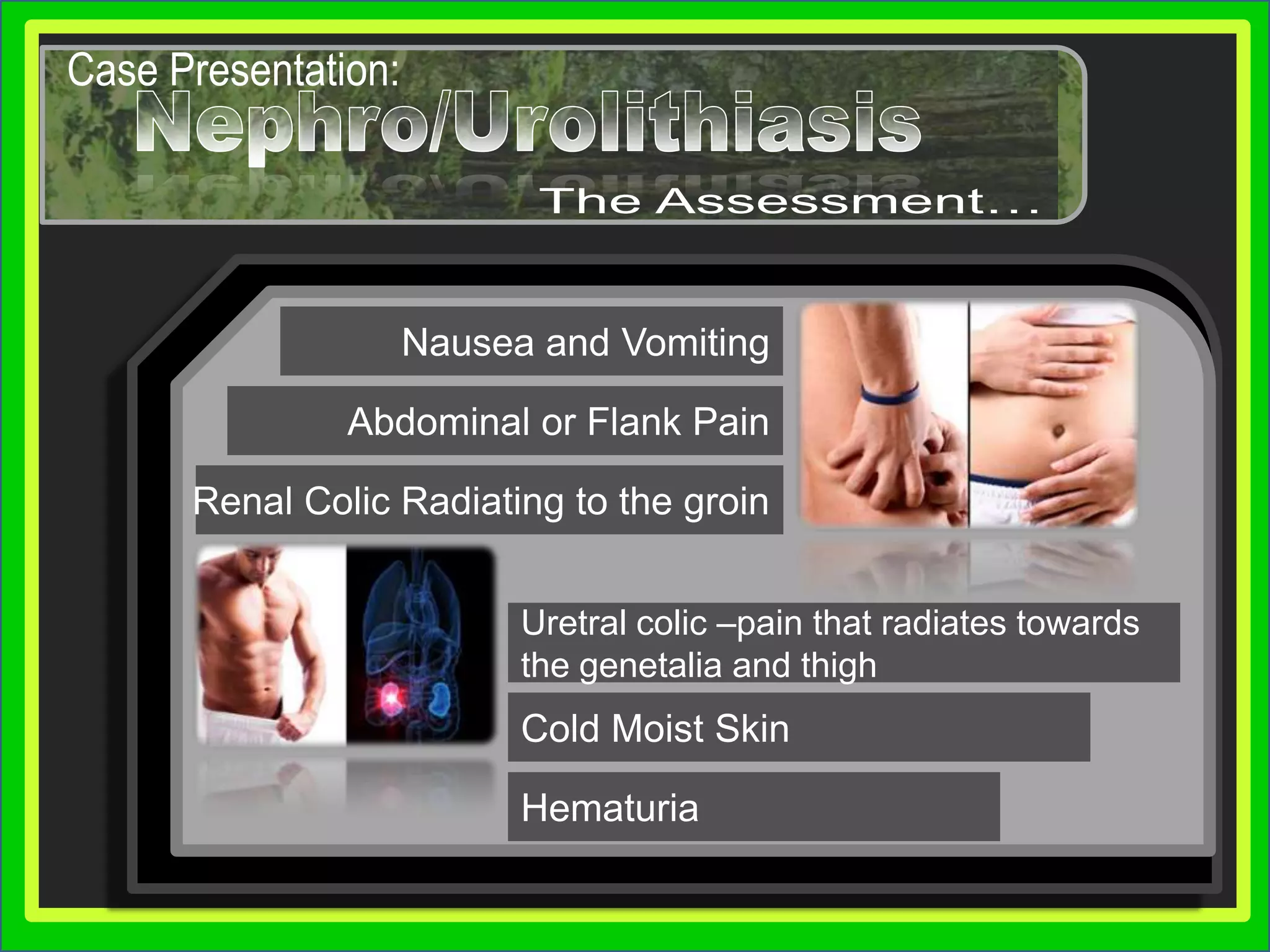
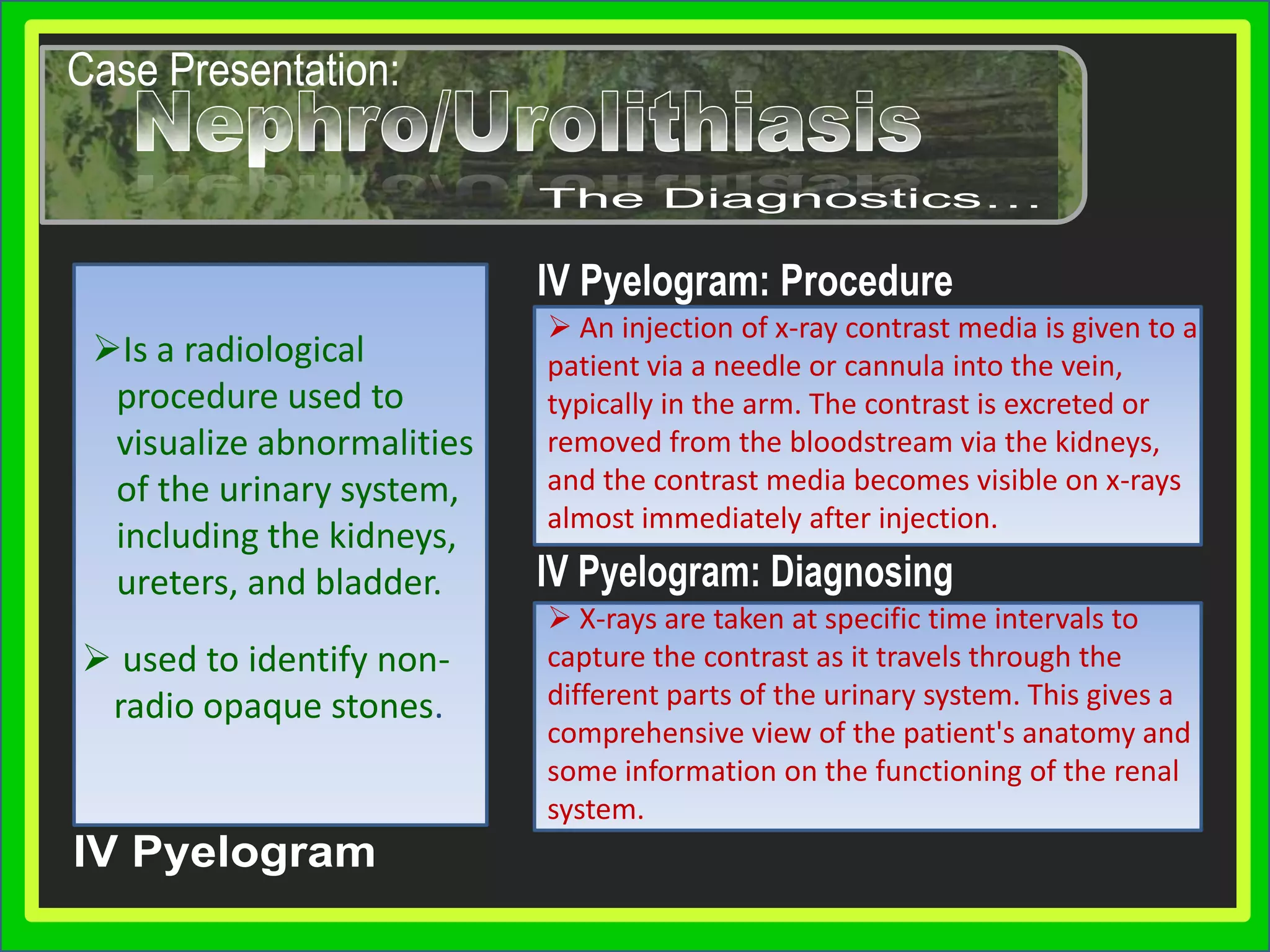
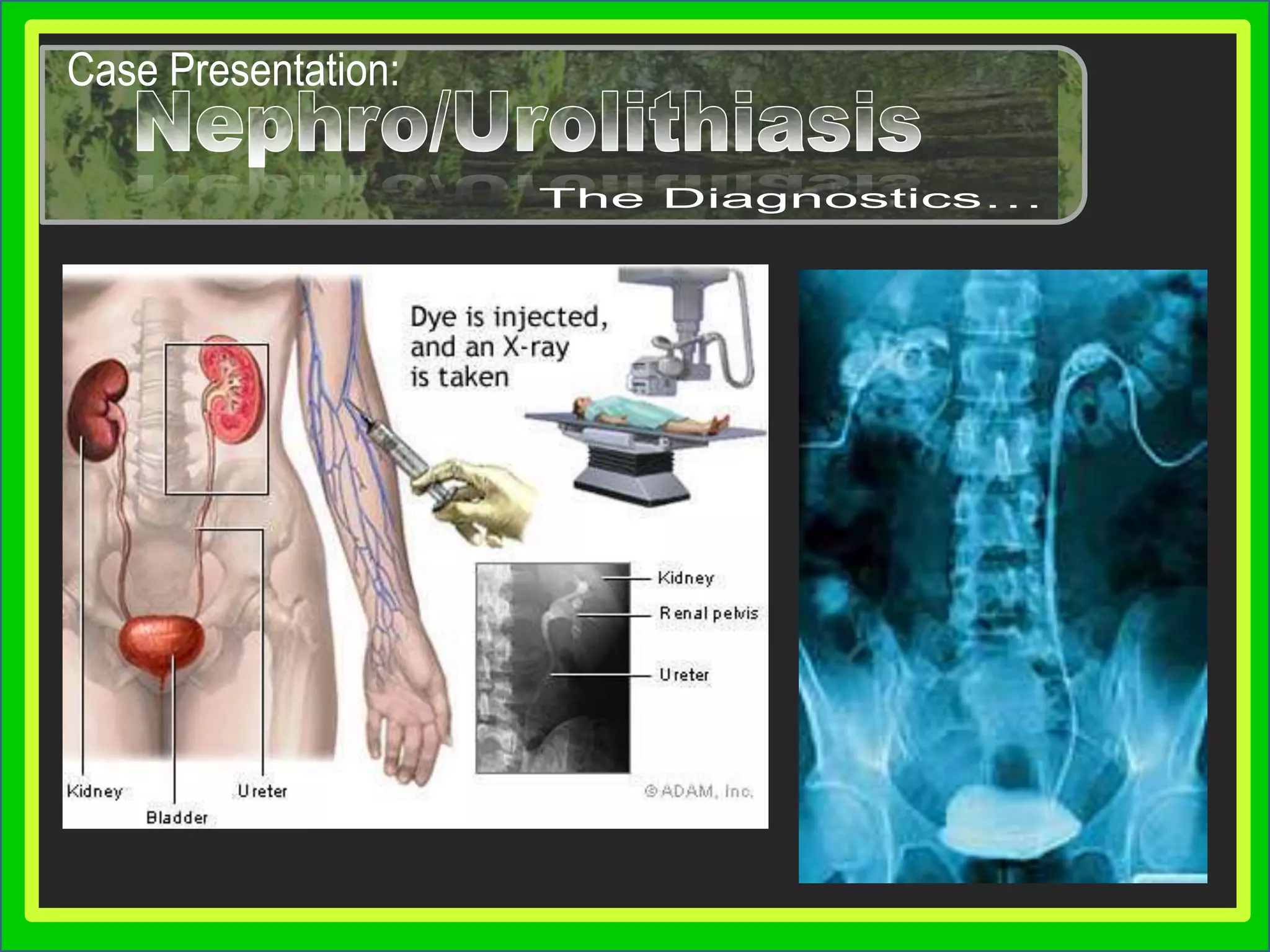
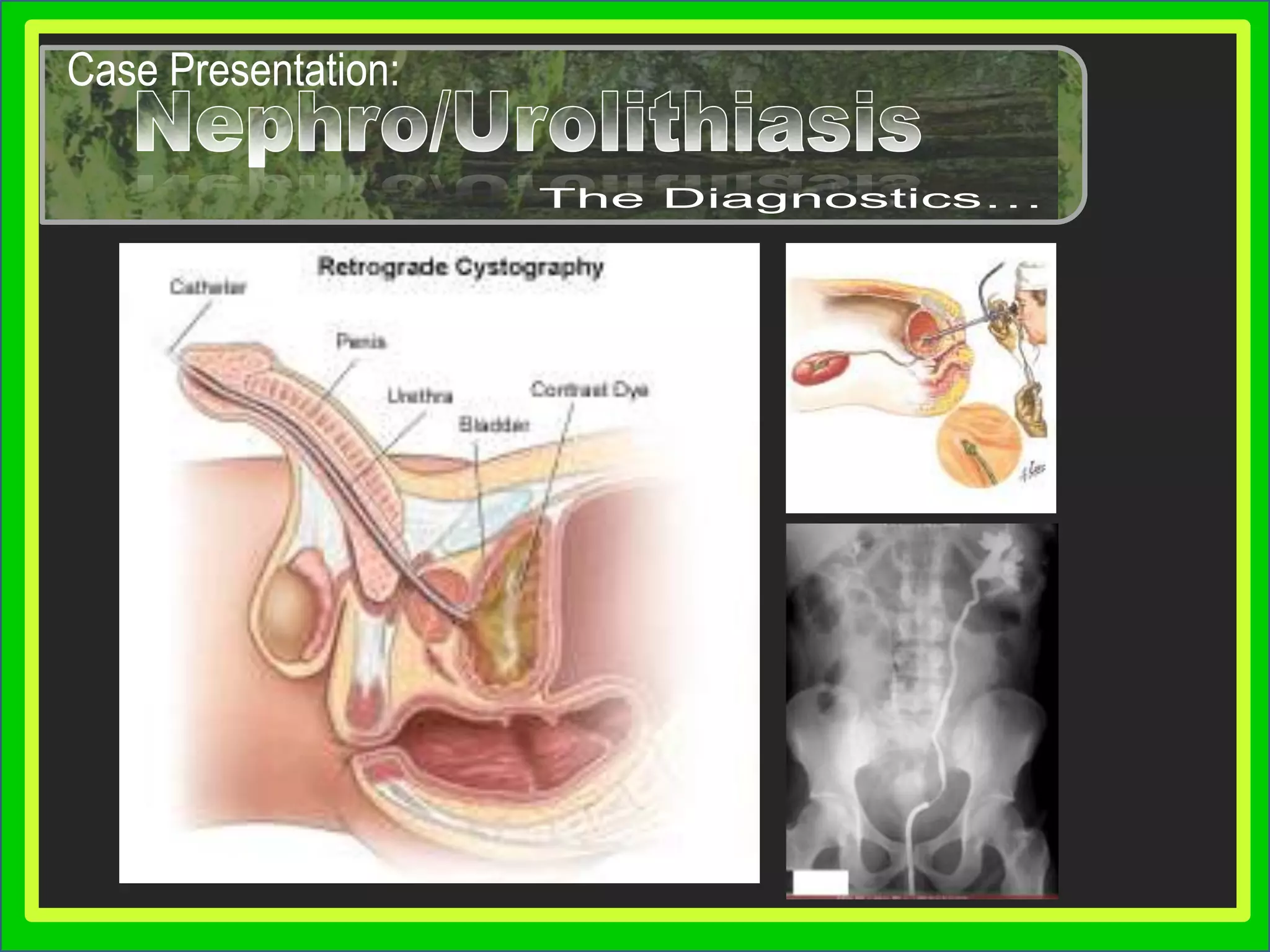
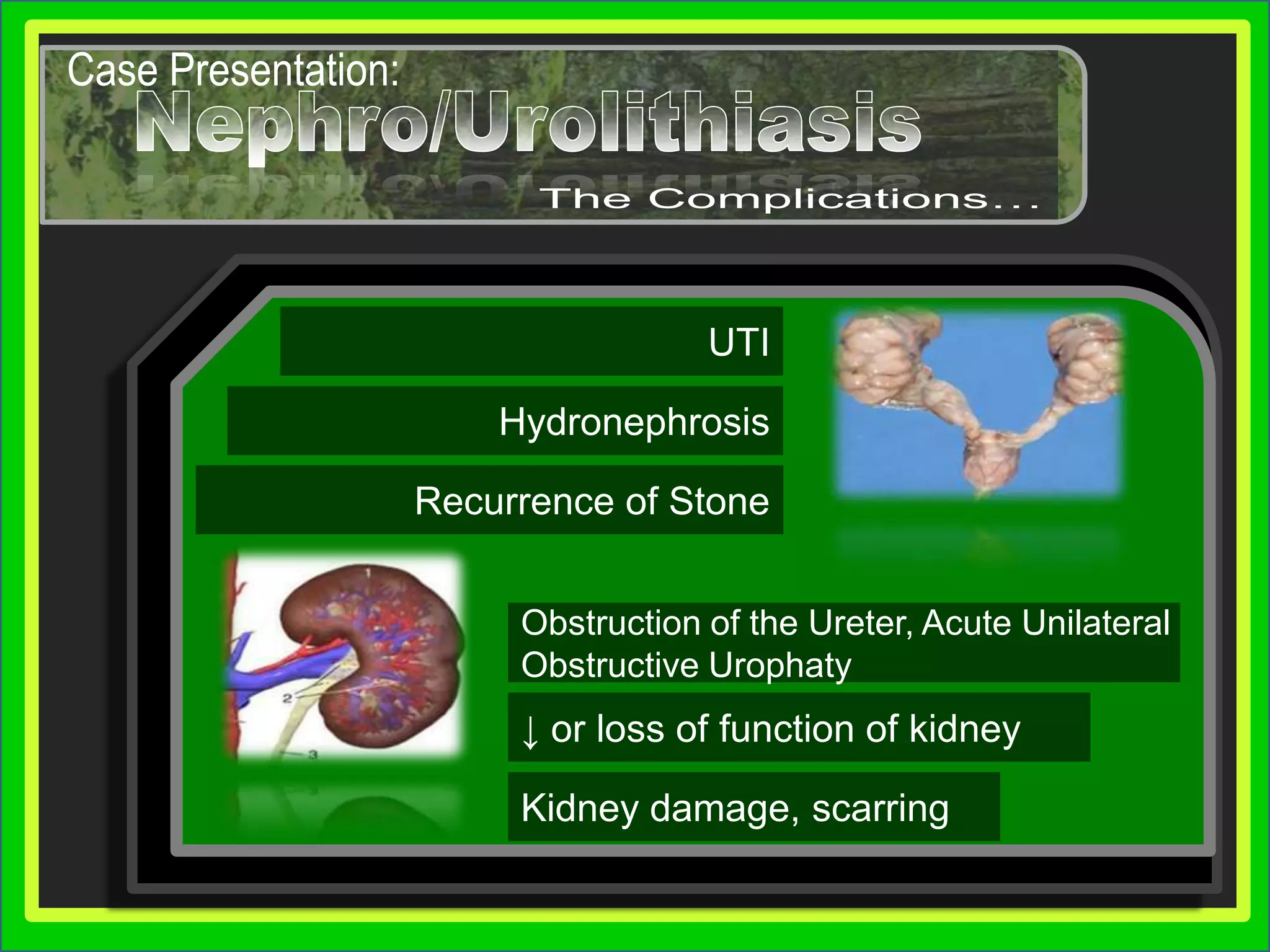
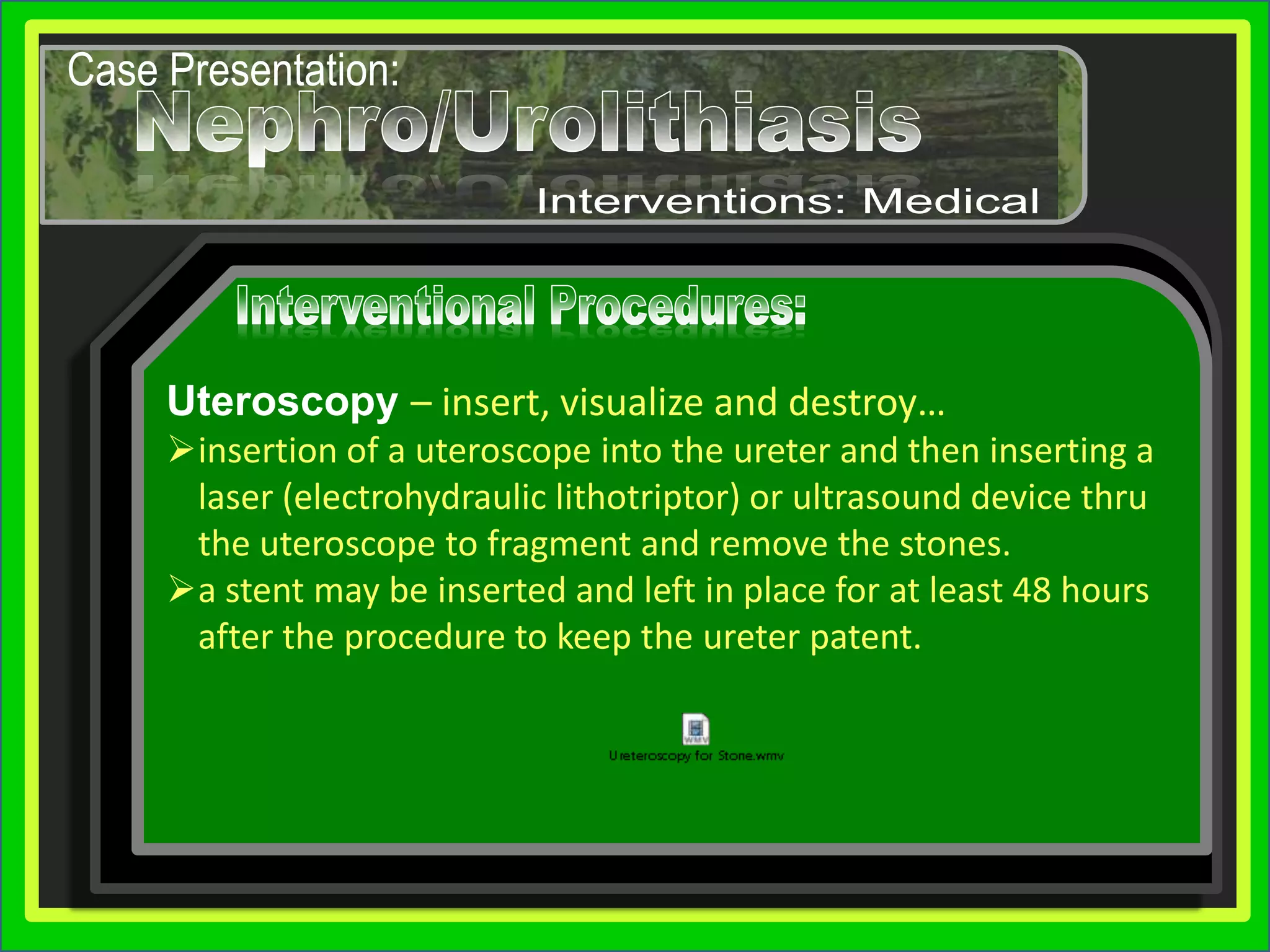
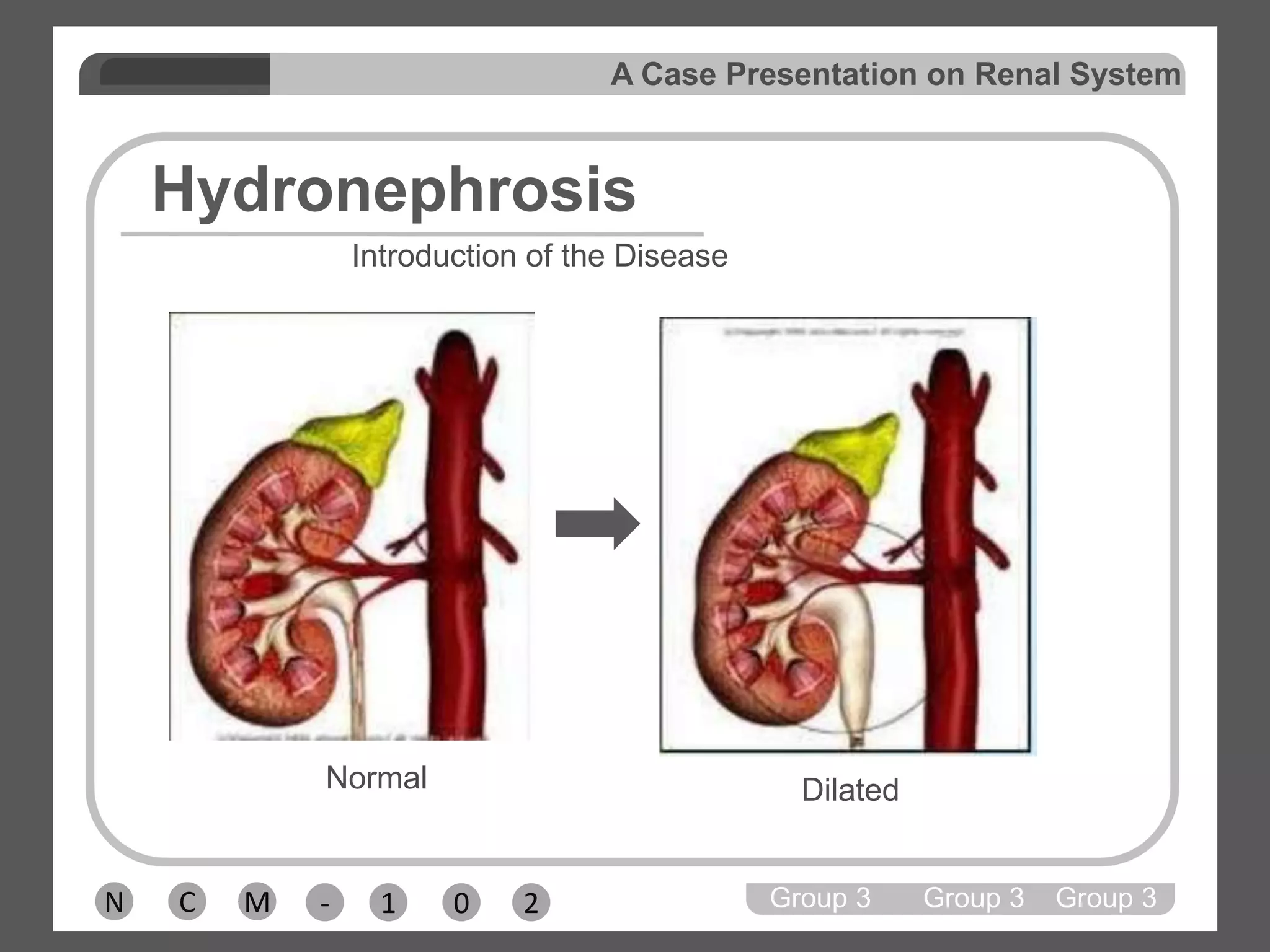
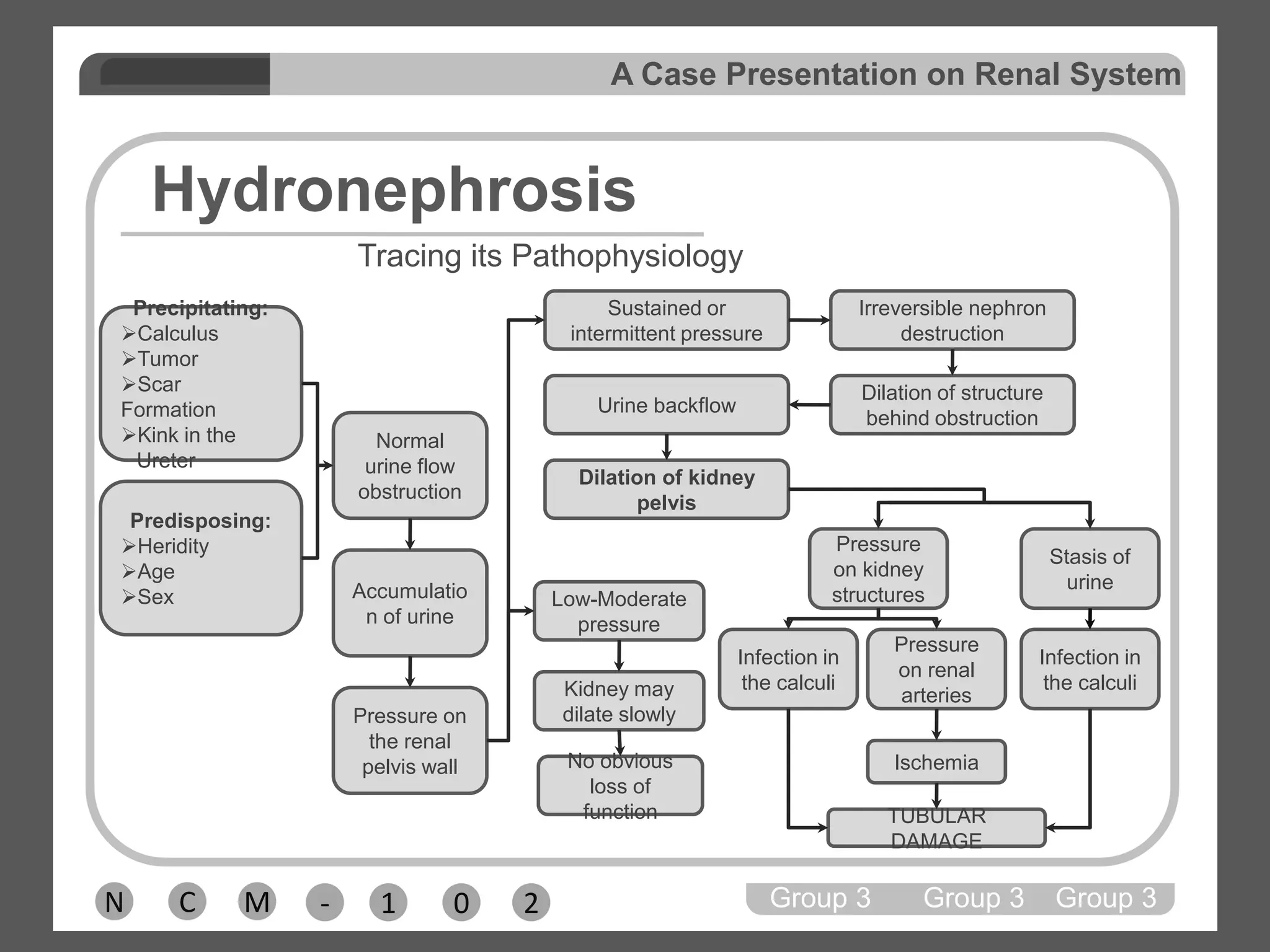
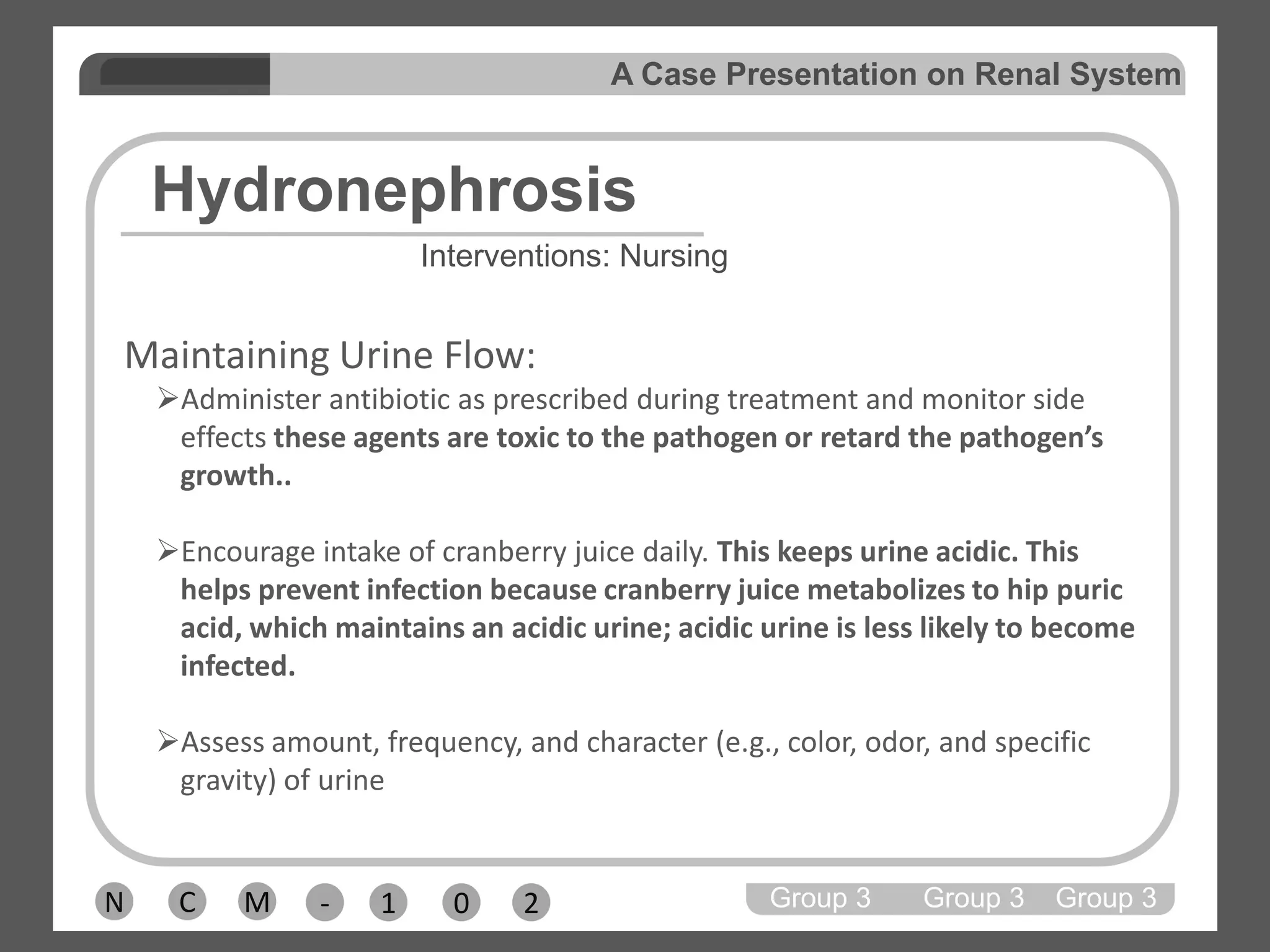
Group 3 presented on nephrolithiasis, urolithiasis, and hydronephrosis. The presentation discussed the conditions, including that nephrolithiasis involves stone formation in the kidney. Diagnostic tests including IV pyelogram, retrograde pyelogram, x-rays, and urine tests were covered. Potential complications from the conditions include UTI, hydronephrosis, stone recurrence, and kidney damage. Nursing interventions focus on relieving pain, increasing fluid intake, educating the patient, and monitoring for complications.